Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology has revolutionized network infrastructure by combining data and power transmission over a single Ethernet cable. However, a PoE switch does not always supply power to connected devices. Instead, it uses an intelligent process to determine if a connected device requires power and is PoE compatible.
How PoE switches work
PoE switches integrate power sourcing equipment (PSE) functionality, enabling them to power a wide range of devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points.
Key components of a PoE switch include:
Detection Mechanism:
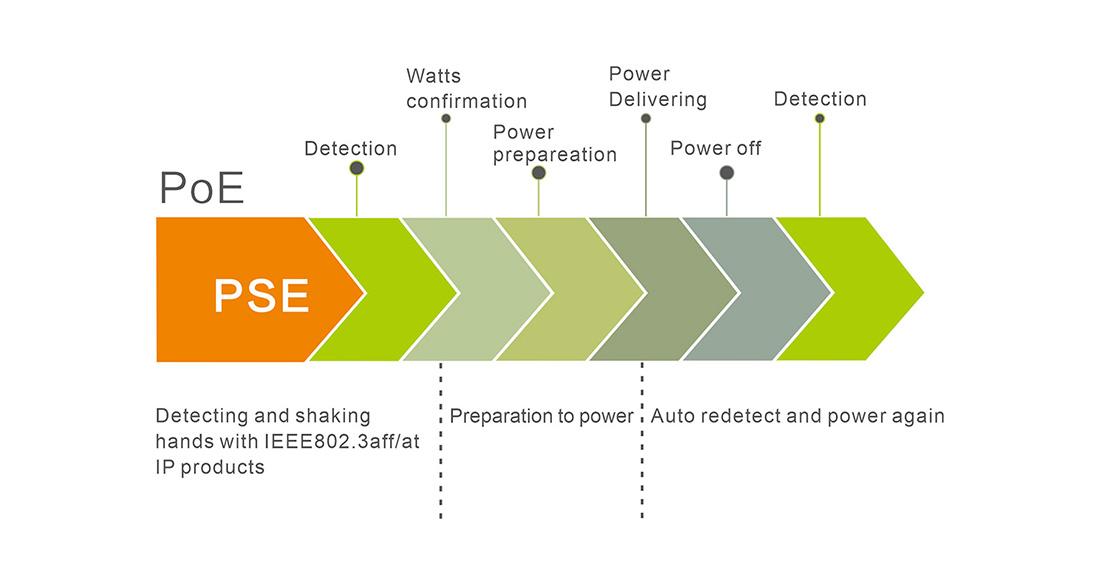
Low-voltage signal: When a device is connected to a PoE port, the switch sends a low-voltage signal to detect if the device is PoE compatible. Only devices that respond appropriately (compliant with IEEE 802.3af/at standards) are powered on.
Power Classification:
Power Requirements: The switch evaluates the power requirements of connected devices. For example, devices may be classified into different power classes, from Class 0 (default) to Class 4 (for PoE+ devices), to allocate the appropriate power.
Power Delivery:
Controlled Powering: Once a device is verified as PoE-compatible and its power requirements are determined, the switch provides the necessary power. This controlled powering ensures efficient use of energy and device safety.
Situations where a PoE switch does not deliver power
Non-PoE devices:
Devices that do not support the PoE standard will not draw power from the PoE switch. A detection mechanism ensures that only PoE-compatible devices receive power, preventing damage to non-PoE devices.
Power Budget Limitation:
PoE switches have a maximum power budget that cannot be exceeded. For example, a switch with a power budget of 65W can power multiple devices, but if the cumulative power requirements exceed this budget, some devices may not receive power.
Extended Mode Feature:
Some PoE switches have an extended mode setting, such as the SP5200-4PFE2FE PoE switch that allows power delivery over longer distances (up to 250 meters) while managing power distribution. In this mode, power distribution is strictly controlled to ensure that all devices within range receive adequate power.
Benefits of Selective Powering
Energy Efficiency:
By supplying power only to necessary devices, PoE switches help reduce overall energy consumption, thereby saving costs and reducing carbon footprint.
Security:
The detection and classification process protects the switch and connected devices from potential damage caused by inappropriate power levels.
Network Flexibility:
PoE technology allows for flexible placement of devices such as IP cameras and access points without the need for nearby power outlets, simplifying network installation and expansion.
PoE switches are designed to intelligently manage power delivery, ensuring that only compatible devices receive the power they need. This not only improves the efficiency and security of network deployment, but also provides flexibility and scalability for applications such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, wireless access points (WAPs), network switches and routers. By understanding the detection mechanism, power classification, and controlled power delivery of PoE technology, network administrators can make informed decisions to deploy PoE switches to optimize their network infrastructure.